The Leader's Role in Advancing Through the Phases of Team Development
Using Bruce Tuckman's Phases of Team Development
29 January 2018
This is an older edition. The most current (2026) edition is available here.
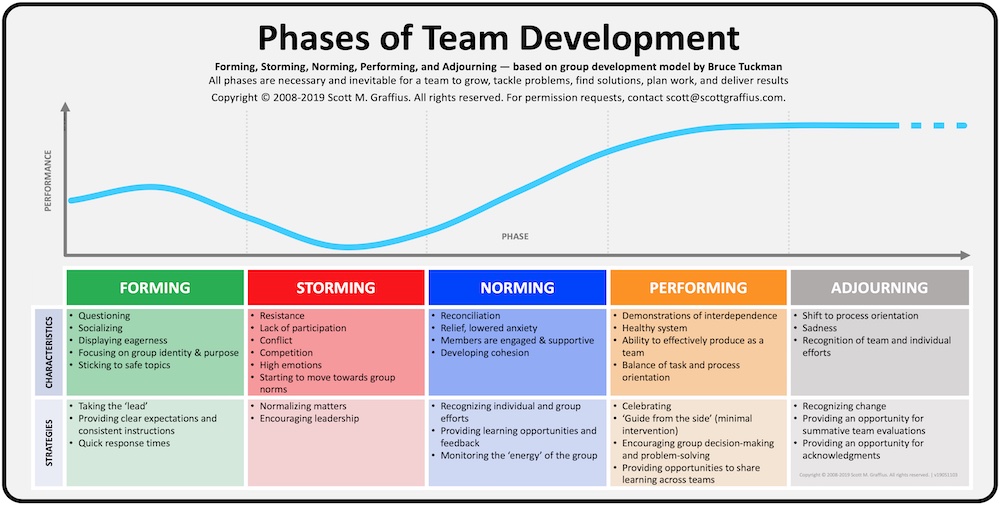
Teams go through stages of development, and Bruce Tuckman established a popular framework on the subject. According to Tuckman, all phases—Forming, Storming, Norming, Performing, and Adjourning—are necessary for the team to grow, tackle problems, find solutions, plan work, and deliver results. This article provides a brief overview of the model, including descriptions and strategies for each phase.

1. Forming
Characteristics of Forming include questioning, socializing, displaying eagerness, focusing on group identity and purpose, and sticking to safe topics. Strategies for this phase include taking the 'lead,' providing clear expectations and consistent instructions, and quick response times.
2. Storming
Traits of Storming include resistance, lack of participation, conflict, competition, high emotions, and moving towards group norms. Strategies for this stage include normalizing matters and encouraging leadership.
3. Norming
Features of Norming include reconciliation, relief, lowered anxiety, members are engaged and supportive, and developing cohesion. Strategies for this phase include recognizing individual and group efforts, providing learning opportunities and feedback, and monitoring the 'energy' of the group.
4. Performing
Characteristics of Performing include demonstrations of interdependence, healthy system, ability to effectively produce as a team, and balance of task and process orientation. Strategies for this stage include celebrating, 'guide from the side' (minimal intervention), encouraging group decision-making and problem-solving, and providing opportunities to share learning across teams.
5. Adjourning
Traits of Adjourning include a shift to process orientation, sadness, and recognition of team and individual efforts. Strategies for this phase include recognizing change, providing an opportunity for summative team evaluations, and providing an opportunity for acknowledgments.

The illustration summarizes the above information—and it shows how performance fluctuates as teams move through each phase. This information may be helpful for looking at your team.

Permission Request Information
To request permission to use the 'Phases of Team Development' visual, contact Scott M. Graffius. If approved, high resolution JPG and PNG image files will be provided, subject to terms and conditions.

Copyright © Scott M. Graffius. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without the express written permission of Scott M. Graffius.

The Spanish Version of the 'Phases of Team Development' -- 'Fases del Desarrollo del Equipo' -- Now Available
19 October 2021
Phases of Team Development
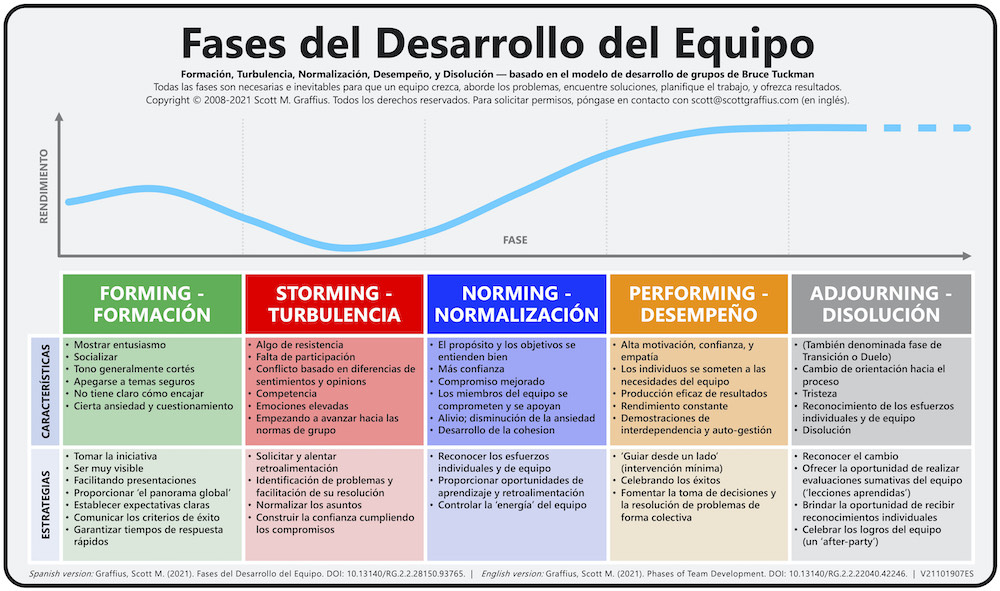
Teams go through phases of development, and Dr. Bruce Tuckman established a popular and durable framework on the subject. According to Dr. Tuckman, all phases—Forming, Storming, Norming, Performing, and Adjourning—are necessary for teams to grow, tackle problems, find solutions, plan work, and deliver results.
Agile project management thought leader, influencer, and author Scott M. Graffius developed a related custom illustration, Phases of Team Development. It highlights the performance level, characteristics, and proven strategies for each of the phases. Project Managers, Scrum Masters, Agile Coaches, DevOps Leads, and other professionals can apply the information to help handle challenges or issues experienced by teams. By doing so, they’ll advance the teams' happiness and productivity, as well as the teams' (and their own) success. Graffius updates the content periodically.
Graffius translated his 'Phases of Team Development' intellectual property into Spanish: 'Fases del Desarrollo del Equipo' — Formación (Forming), Turbulencia (Storming), Normalización (Norming), Desempeño (Performing), and Disolución (Adjourning).
Sometimes, different words are used for the phases. For example, 'Storming' is translated as 'Turbulencia' — but 'Conflicto' or other alternatives are occasionally used instead. This article and the related Fases del Desarrollo del Equipo illustration incorporate the selections for phases referenced in the Spanish version of the Project Management Institute's A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge. The five phases in Spanish are: Formación, Turbulencia, Normalización, Desempeño, y Disolución.
More on the Spanish version follows.


Permission Request Information
For permission requests to use Graffius' 'Fases del Desarrollo del Equipo' visual, contact Scott M. Graffius in English. If your request is approved, Graffius will give you an authorization/license and, if applicable, high-resolution file(s) of the visual.


How to Cite This Article
Graffius, Scott M. (2021, October 19). The Spanish Version of the 'Phases of Team Development' -- 'Fases del Desarrollo del Equipo' -- Now Available. Available at: https://scottgraffius.com/blog/files/equipo-21.html.
How to Cite Only the Visual
Graffius, Scott M. (2021). Fases del Desarrollo del Equipo. Digital Object Identifier (DOI): 10.13140/RG.2.2.28150.93765. DOI link: https://dx.doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.28150.93765.


For information on the English version of the Phases of Team Development, visit here.

About Scott M. Graffius

Scott M. Graffius, PMP, CSP-SM, CSP-PO, CSM, CSPO, SFE, ITIL, LSSGB is an agile project management practitioner, consultant, award-winning author, and international speaker. He has generated over one billion dollars of business value in aggregate for the organizations he has served. Graffius is the founder, CEO, and principal consultant at Exceptional PPM and PMO Solutions™ and subsidiary Exceptional Agility™, based in Los Angeles, California. His expertise spans project, program, portfolio, and PMO leadership inclusive of agile, traditional, and hybrid approaches. Content from his books, workshops, speaking engagements, and more have been featured and used by businesses, governments, and universities including Gartner, Microsoft, Deloitte, Oracle, Cisco, Ford, Qantas, Atlassian, Bayer, the National Academy of Sciences, the United States Department of Energy, the United States Army, Project Management Institute, the IEEE, the New Zealand Ministry of Education, Tufts University, Texas A&M University, Virginia Tech, Penn State, Warsaw University of Technology, University of Waterloo, Loughborough University London, and others. Graffius has spoken at 58 conferences and other events around the world, including Armenia, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, India, Ireland, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Netherlands, New Zealand, Sweden, United Kingdom, and the United States. Thinkers360 named Graffius a global top thought leader and influencer in four domains: Agile, Change Management, Digital Transformation, and GovTech.
His full bio is available here.
Connect with Scott on:



Copyright
Copyright © Scott M. Graffius. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without the express written permission of Scott M. Graffius.

Bruce Tuckman’s Model (Forming, Storming, Norming, Performing, and Adjourning) is Highly Relevant and Beneficial, But It Doesn’t Please Everyone
08 November 2021
Names and certain identifying details are not included or are redacted (replaced with black rectangles) to respect privacy.

The Question
Steve Jobs famously said: “You can please some of the people some of the time” in response to a tough question at the 1997 Worldwide Developer Conference. The following experience reminded me of that quote.
In a recent workshop on team leadership, a student asked me, “What do you think about █████████’s disregard of Tuckman’s model?” (Note: The student was referring to a person who's a leader in Agile and Scrum. That person's name is redacted, subsequently referred to as “critic.” His or her stance seems to be the rare exception.) I’m detailing my response here.

The Background for Context
Bruce Tuckman (Ph.D. in Psychology from Princeton University) conducted extensive research on group dynamics, and he published a related model in 1965. At that time, the model included four phases: forming, storming, norming, and performing. However, Dr. Tuckman subsequently determined that adjourning was so important that he (with Mary Ann Jensen) updated his model in 1977 to add adjourning as the fifth phase. In the context of this discussion, phases and stages may be used interchangeably; and group dynamics is also referred to as group development, team dynamics, and team development.
Dr. Tuckman’s model has stood the test of time because it remains highly relevant and beneficial. Since his related work was published, it has been supported by additional peer-reviewed research. And it has received recommendations and coverage from leading organizations including Google, Harvard Business Review, IEEE, Forbes, MIT, Fast Company, NASA, Microsoft, TNW, Project Management Institute, Scrum Alliance, Scrum.org, Association for Project Management, Gartner, CIO, Spotify, Imperial College London, RAND Corporation, Princeton University, Software Engineering Institute, University of Edinburgh, Cisco, KPMG, Warsaw University of Technology, DevOps Institute, American Express, SANS Institute, Zurich University, SAP, ViacomCBS, Oxford University, American Management Association, AT&T, University of Southern California, IBM, and many others.
While Tuckman’s model is durable and relevant, no model is perfect. It can be helpful to understand any concerns or limitations—with an emphasis on any which are independently verifiable and are published in peer-reviewed studies.
I related to the student that there are critics of Tuckman’s model, but that they’re few—and I’m not familiar with criticisms meeting the aforementioned rigor of being independently verifiable with such findings appearing in peer-reviewed studies.
I said, for example, that I was already aware of the critic's stated disregard of Bruce Tuckman’s model. I previously looked into the situation to learn more. My research and findings follow.

The Research and Findings
In a █████ communication, the critic said “I never liked ...” referring to Tuckman’s model. He or she went on to state that his or her reason was that “Gersick tested it ...” (Tuckman’s model) and “...it’s not true.” The critic included a link to the paper which was the basis for his or her stance. The link goes to the following paper:
Curtis, B., Walz, D., and Elam, J. (1990, October 1). Studying the Process of Software Design Teams. In: ISPW '90: Proceedings of the 5th International Software Process Workshop on Experience with Software Process Models, pages 52-53.
The critic said that “Gersick tested it” and pointed to the paper. However, Gersick is not an author on the paper. Still, I reviewed the content to see what, if anything, the authors (Curtis, Walz, and Elam) said about Tuckman, Tuckman’s model, and/or Gersick. Here’s what I found.
On Tuckman: Tuckman was not mentioned anywhere in the paper.
On Tuckman’s model (a reference to forming, storming, norming, performing, and/or adjourning): The following appears: “Rather than the standard group process of form-storm-norm-perform, Gersick suggested there came a point halfway through a group project where the team faced its lack of progress.”
On Gersick: Gersick was mentioned four times: “Gersick (1988) observed such a point in a study of project teams” and “Rather than the standard group process of form-storm-norm-perform, Gersick suggested there came a point halfway through a group project where the team faced its lack of progress” and “Gersick's model may be more descriptive of temporary teams that are asked to perform tasks out of their area of expertise” and (a reference citation) “Gersick, C.J.G. (1988). Time and Transition in Work Teams: Toward a New Model of Work Development. Academy of Management Journal, 31 (1), 9-41.”
The critic said that “Gersick tested it” ... and “...it’s not true.” However, as a summary of the above, Gersick is not the author of the paper, and the authors (Curtis, Walz, and Elam) commented that Tuckman’s model did not seem to work for one project. On that one project, “Rather than ... form-storm-norm-perform ... there came a point halfway through ... where the team faced its lack of progress.” That does not negate Tuckman’s model. While teams typically move through the different phases, it’s entirely possible for a team to face a lack of progress at a given time. Phases don’t progress magically; the phase is a marker of the team’s current progress and effectiveness. The critic said that “Gersick tested it” ... and “...it’s not true.” The research specified by the critic did not state that it tested Tuckman’s model and found it to not be true. The research specified by the critic does not support his or her stand. Nevertheless, I dug deeper.
The above paper by Curtis, Walz, and Elam includes Gersick’s work as a reference. I found and carefully reviewed Gersick’s respective research. Again, it’s: “Gersick, C.J.G. (1988). Time and Transition in Work Teams: Toward a New Model of Work Development. Academy of Management Journal, 31 (1), 9-41.” I looked to see what Gersick said about Tuckman or his model. Here’s what I discovered.
Tuckman was mentioned five times: “There was no initial ‘storming’ (Tuckman, 1965; Tuckman & Jensen, 1977) in this group” and “First, as Tuckman pointed out in 1965 and others have noted up to the present (Hare, 1976; McGrath, 1986; Poole, 1983b), they offer snapshots of groups at different points in their life-spans but say little about the mechanisms of change” and “Since all teams were doing construction work on their projects during phase 2, similar to ‘performing’ in Tuckman’s (1965) synthesis, it was a time when teams were more similar to both each other and to the traditional model than they were in phase 1” and (a reference citation) “Tuckman, B. 1965. Developmental Sequence in Small Groups. Psychological Bulletin, 63: 384-399” and (another reference citation) “Tuckman, B., & Jensen, M. 1977. Stages of Small-Group Development. Group and Organizational Studies, 2: 419-427.”
The critic said that “Gersick tested it” ... and “...it’s not true.” However, as a summary of the above, Gersick did not state that Tuckman’s model was tested and found to not be true. For example, Gersick did not say that there was no storming; rather, it was qualified as “no initial ‘storming.’” Furthermore, and most importantly, Gersick provided the following caveat: “This study must be interpreted with caution. It was hypothesis-generating, not hypothesis-testing; the model is expressly provisional.” According to Gersick, the research did not test or prove anything.
The research—both the paper pointed to by the critic, and the reference study—does not supply the stated basis for the critic's stance.

The Conclusion with the Answer
In conclusion, Tuckman’s model has stood the test of time because it remains highly relevant and beneficial. No model is perfect, and it is helpful to understand any concerns or limitations—with an emphasis on any which are independently verifiable and are published in peer-reviewed studies.
My answer to the student’s question (“What do you think about █████████’s disregard of Tuckman’s model?”) was that I diligently reviewed the facts and neither the paper linked to by the critic, nor the other study cited by the paper, support the critic’s assertion that “Gersick tested it ...” (Tuckman’s model) and “...it’s not true.”
Maybe—or maybe not—the critic's view of the model is because of a misunderstanding regarding the research. Or maybe—or maybe not—there's another reason. As Steve Jobs said, “You can please some of the people some of the time.”



The Phases of Team Development Visual
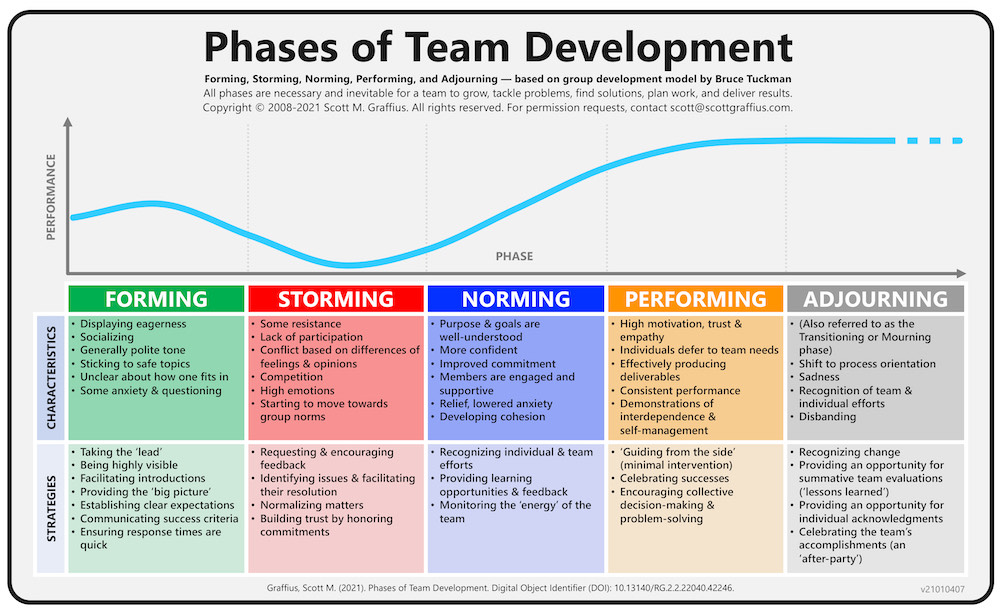
🔥 Update: The newest version is here.

About Scott M. Graffius

Scott M. Graffius, PMP, CSP-SM, CSP-PO, CSM, CSPO, SFE, ITIL, LSSGB is an agile project management practitioner, consultant, award-winning author, and international speaker. He has generated over 1.75 billion dollars of business value in aggregate for the organizations he has served. Graffius is the founder, CEO, and principal consultant at Exceptional PPM and PMO Solutions™ and subsidiary Exceptional Agility™, based in Los Angeles, California. His expertise spans project, program, portfolio, and PMO leadership inclusive of agile, traditional, and hybrid approaches. Content from his books (Agile Scrum and Agile Transformation), workshops, speaking engagements, and more have been featured and used by businesses, governments, and universities including Gartner, Microsoft, Deloitte, Oracle, Cisco, Ford, Qantas, Atlassian, Bayer, the National Academy of Sciences, the United States Department of Energy, the United States Army, Project Management Institute, the IEEE, the New Zealand Ministry of Education, Tufts University, Texas A&M University, Virginia Tech, Penn State, Warsaw University of Technology, University of Waterloo, Loughborough University London, and others. Graffius has spoken at 58 conferences and other events around the world, including Armenia, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, India, Ireland, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Netherlands, New Zealand, Sweden, United Kingdom, and the United States. Thinkers360 named Graffius a global top thought leader and influencer in four domains: Agile, Change Management, Digital Transformation, and GovTech.
His full bio is available here.
Connect with Scott on:


About Agile Scrum: Your Quick Start Guide with Step-by-Step Instructions

Shifting customer needs are common in today's marketplace. Businesses must be adaptive and responsive to change while delivering an exceptional customer experience to be competitive.
There are a variety of frameworks supporting the development of products and services, and most approaches fall into one of two broad categories: traditional or agile. Traditional practices such as waterfall engage sequential development, while agile involves iterative and incremental deliverables. Organizations are increasingly embracing agile to manage projects, and best meet their business needs of rapid response to change, fast delivery speed, and more.
With clear and easy to follow step-by-step instructions, Scott M. Graffius's award-winning Agile Scrum: Your Quick Start Guide with Step-by-Step Instructions helps the reader:
- Implement and use the most popular agile framework―Scrum;
- Deliver products in short cycles with rapid adaptation to change, fast time-to-market, and continuous improvement; and
- Support innovation and drive competitive advantage.
Hailed by Literary Titan as “the book highlights the versatility of Scrum beautifully.”
Winner of 17 first place awards.
Agile Scrum: Your Quick Start Guide with Step-by-Step Instructions is available in paperback and ebook/Kindle in the United States and around the world. Some links by country follow.
- 🇧🇷 Brazil
- 🇨🇦 Canada
- 🇨🇿 Czech Republic
- 🇩🇰 Denmark
- 🇫🇮 Finland
- 🇫🇷 France
- 🇩🇪 Germany
- 🇬🇷 Greece
- 🇭🇺 Hungary
- 🇮🇳 India
- 🇮🇪 Ireland
- 🇮🇱 Israel
- 🇮🇹 Italy
- 🇯🇵 Japan
- 🇱🇺 Luxembourg
- 🇲🇽 Mexico
- 🇳🇱 Netherlands
- 🇳🇿 New Zealand
- 🇳🇴 Norway
- 🇪🇸 Spain
- 🇸🇪 Sweden
- 🇨🇭 Switzerland
- 🇦🇪 UAE
- 🇬🇧 United Kingdom
- 🇺🇸 United States

About Agile Transformation: A Brief Story of How an Entertainment Company Developed New Capabilities and Unlocked Business Agility to Thrive in an Era of Rapid Change

Thriving in today's marketplace frequently depends on making a transformation to become more agile. Those successful in the transition enjoy faster delivery speed and ROI, higher satisfaction, continuous improvement, and additional benefits.
Based on actual events, Agile Transformation: A Brief Story of How an Entertainment Company Developed New Capabilities and Unlocked Business Agility to Thrive in an Era of Rapid Change provides a quick (60-90 minute) read about a successful agile transformation at a multinational entertainment and media company, told from the author's perspective as an agile coach.
The award-winning book by Scott M. Graffius is available in paperback and ebook/Kindle in the United States and around the world. Some links by country follow.
- 🇦🇺 Australia
- 🇦🇹 Austria
- 🇧🇷 Brazil
- 🇨🇦 Canada
- 🇨🇿 Czech Republic
- 🇩🇰 Denmark
- 🇫🇮 Finland
- 🇫🇷 France
- 🇩🇪 Germany
- 🇬🇷 Greece
- 🇮🇳 India
- 🇮🇪 Ireland
- 🇯🇵 Japan
- 🇱🇺 Luxembourg
- 🇲🇽 Mexico
- 🇳🇱 Netherlands
- 🇳🇿 New Zealand
- 🇪🇸 Spain
- 🇸🇪 Sweden
- 🇨🇭 Switzerland
- 🇦🇪 United Arab Emirates
- 🇬🇧 United Kingdom
- 🇺🇸 United States

The short URL for this article is: https://bit.ly/tckmn
Posts related to this article are on Twitter and Instagram (via @AgileScrumGuide)
© Copyright 2021 Scott M. Graffius. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without the express written permission of Scott M. Graffius.

